
Journal of Agronomic Education 14(2): 84–90. Expressing cation exchange capacity in milliequivalents per 100 grams and in SI units. Soil Fertility and Fertilizers, 8th Edition. publications/ohio-agronomy-guide-15th-edition-bulletin-472 Ohio State University Extension Bulletin 472. While standard soil testing laboratories commonly calculate and report these values in soil test reports, it is helpful to have a solid understanding of CEC and base saturation calculations.
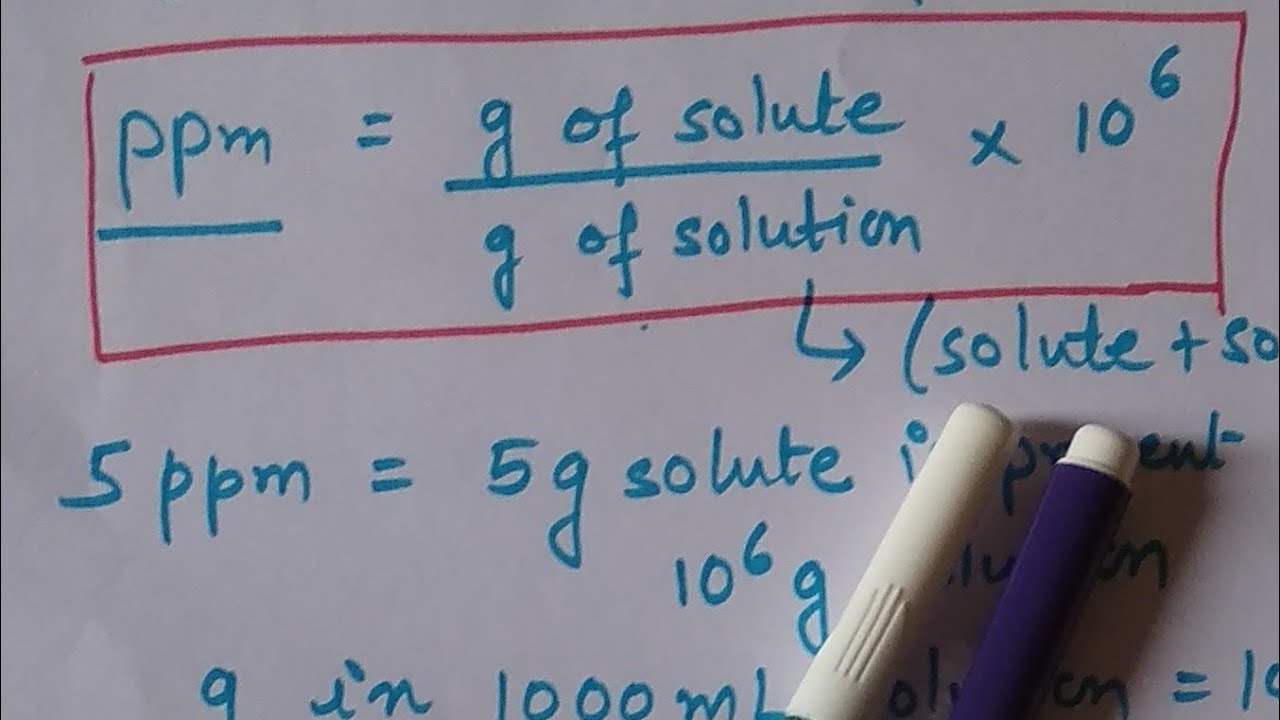
Base saturation is closely related to pH as base saturation increases, pH increases.īase Saturation (%) = ( Base cations/CEC) \( x \text \)Ĭation exchange capacity and base saturation are important soil measurements that help determine how a soil is managed and fertilized. Therefore, it has a higher base saturation. PPM is commonly measured by a grower using an electronic pen which measures the electrical conductivity of the water (EC). Basically the idea is to quantify how much stuff is in your water. Figure 2 shows two soils with the same CEC, but the soil on the right has more base cations (in blue). Understanding and Calculating Nutrient PPM PPM (Parts Per Million) can seem like a mystery but it’s actually very simple. (Ca 2+ + Mg 2+ + K + + Na +) + (H + + Al 3+ + NH 4 +)įigure 1 illustrates a low CEC soil, with a small number of negative charges and associated cations (left) and a high CEC soil with a larger amount of negative charges, occupied by a greater number of total cations (right).īase saturation is calculated as the percentage of CEC occupied by base cations. equilibrated classical carbocations the difference is usually 2350 ppm. Exchangeable cations include base cations, calcium (Ca 2+), magnesium (Mg 2+), potassium (K +) and sodium (Na +), as well as acid cations such as hydrogen (H +), aluminum (Al 3+) and ammonium (NH 4 +). They calculate the difference between the sum of the chemical shifts of all the. It is measured commonly in commercial soil testing labs by summing cations (positively charged ions that are attracted to the negative surface charges in soil). The relationship between soil texture and CECĬation exchange capacity is defined as a soil’s total quantity of negative surface charges. Values over 25 meq/100 g soil are found with heavy clay soils, organic, or muck soils. Soils in Ohio can encompass a wide CEC range, but typically fall somewhere between 5 to 25 meq/100 g soil (Table 1). Soil CEC typically increases as clay content and organic matter increase because cation exchange occurs on surfaces of clay minerals, organic matter, and roots. It is the potential of available nutrient supply, not a direct measurement of available nutrients. Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)Ĭation exchange capacity (CEC) is a fundamental soil property used to predict plant nutrient availability and retention in the soil.

The purpose of this fact sheet is to define soil cation exchange capacity, base saturation and calcium saturation, and demonstrate how these values are calculated in soil test reports.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
